New SNAP Rules Start: The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as food stamps, is an essential support system for millions of Americans, ensuring access to nutritious food for individuals and families facing financial hardships. The program has seen several changes over the years, and with the new SNAP rules starting in January 2026, there are some significant adjustments to both eligibility criteria and how benefits can be used. Understanding these updates is crucial for anyone who currently relies on SNAP or is considering applying in the future. Whether you’re a SNAP recipient, a social worker, or a professional in the field, understanding the 2026 updates will help you navigate the process, ensure continued eligibility, and adjust to changes that might impact your food purchasing options. This article delves deep into the new rules, providing you with everything you need to know about SNAP eligibility, work requirements, food restrictions, and other vital details.
Table of Contents
New SNAP Rules Start
The new SNAP rules starting in January 2026 will significantly impact the way eligibility is determined, how benefits are distributed, and what recipients can buy with their benefits. With the expanded work requirements, food purchase restrictions, and updated income thresholds, it is crucial for SNAP recipients and professionals to stay informed about these changes. To ensure that you remain eligible for SNAP benefits, check with your local SNAP office for details specific to your state and household. Being proactive about understanding the eligibility guidelines, exemption criteria, and benefit adjustments will help you continue to receive the support you need while adjusting to the new rules.

| Key Update | Details |
|---|---|
| Work Requirements | New work participation requirements for able-bodied adults without dependents (ABAWDs), requiring 80 hours of work per month. Exemptions apply. |
| Food Purchase Restrictions | Several states will enforce bans on non-nutritious foods, including sugary drinks and candy, starting January 1, 2026. |
| Income and Asset Limits | Income thresholds are based on household size and federal poverty levels, with regular updates to eligibility. |
| Benefit Adjustments | Monthly benefits will be adjusted for cost of living increases, providing more support to families struggling with inflation. |
| Administrative Changes | Federal policy changes shifting more administrative costs to states may lead to variations in SNAP eligibility and access depending on where you live. |
| Exemption Categories | Certain exemptions for veterans, the homeless, and former foster youth will remain, but the eligibility criteria are stricter for many adults without dependents. |
| Additional Resources | For more information on eligibility and updates, visit the official SNAP website. |
Understanding the New SNAP Rules Start
1. Work Requirements Are Getting Stricter
One of the most significant changes to SNAP eligibility starting in 2026 involves the work requirement for able-bodied adults without dependents (ABAWDs). Previously, work requirements applied to individuals aged up to 49, but the new rules will extend this requirement to include adults up to age 64. This means that if you are between 18 and 64 years old, and you are not working or participating in an approved activity, you could lose your benefits unless you qualify for one of the exemptions.
The work requirement mandates that eligible adults work or participate in an approved activity for at least 80 hours per month. These activities can include:
- Full-time or part-time employment
- Job training programs
- Volunteering
- Community service
The goal of these changes is to encourage individuals to gain skills, work, and eventually become self-sufficient. While some might find this challenging, there are exemption categories in place to support specific groups:
- Veterans who are in transition
- Homeless individuals
- Former foster youth
- Parents with children under a certain age
For those who do not meet the work requirement and don’t fall into one of these exemption categories, it is crucial to understand that the penalty will likely be the suspension of benefits after a certain period. However, recipients who are unable to work due to specific reasons, such as illness or disability, will still have options to apply for an exemption.
If you’re concerned about meeting these requirements, one way to stay compliant is by enrolling in job training programs or looking for volunteer opportunities in your community. These activities often count toward the monthly work requirement, and they can help you stay on track while contributing to your local community.
2. Food Purchase Restrictions: What Can and Can’t You Buy?
Starting in January 2026, a major change to SNAP benefits will involve food purchase restrictions. Several states have already secured federal waivers to implement bans on the purchase of non-nutritious foods, which includes sugary drinks, candy, and certain snack foods. This initiative is aimed at reducing the consumption of foods that are often high in sugar, fat, and empty calories, in hopes of improving the overall health of SNAP recipients.
Here are the types of foods that may be restricted:
- Sugary drinks, such as soda and energy drinks
- Candy and chocolate bars
- Processed snacks, including chips, cookies, and cakes that have little nutritional value
These changes will not apply universally; rather, the restrictions will vary by state. States such as Indiana, West Virginia, and Utah are among the first to implement these changes. If you live in one of these states, you will need to make adjustments to how you shop, as these products will no longer be eligible for purchase using SNAP benefits.
It’s important to note that these restrictions don’t eliminate the purpose of SNAP, which is to help individuals access nutritious food. You can still purchase:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins, including poultry, fish, and legumes
However, the goal is to encourage a more nutritious lifestyle among SNAP recipients by limiting access to unhealthy foods that contribute to health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
3. Income and Asset Limits: Know the Thresholds
The eligibility for SNAP benefits is determined by your household income and assets. If your income exceeds a certain threshold or if your assets are above the allowed limit, you may not qualify for benefits. These limits are updated regularly to account for changes in the cost of living, and it’s important to be aware of these limits to determine your eligibility.
Here’s a breakdown of the income limits for SNAP:
- Gross income: This is the total income before deductions like taxes and other expenses. The gross income limit is generally 130% of the federal poverty level (FPL) for most households.
- Net income: This is your gross income minus certain deductions, such as housing costs, childcare, and medical expenses. To qualify, your net income must typically be below the federal poverty level.
- Asset limits: In addition to income, the total value of your assets will also be considered. This includes savings, checking accounts, cash, and other resources. Typically, the asset limit is $2,750 for households without elderly or disabled members, and $4,250 for those with elderly or disabled members.
Every year, the income limits and asset thresholds are adjusted.
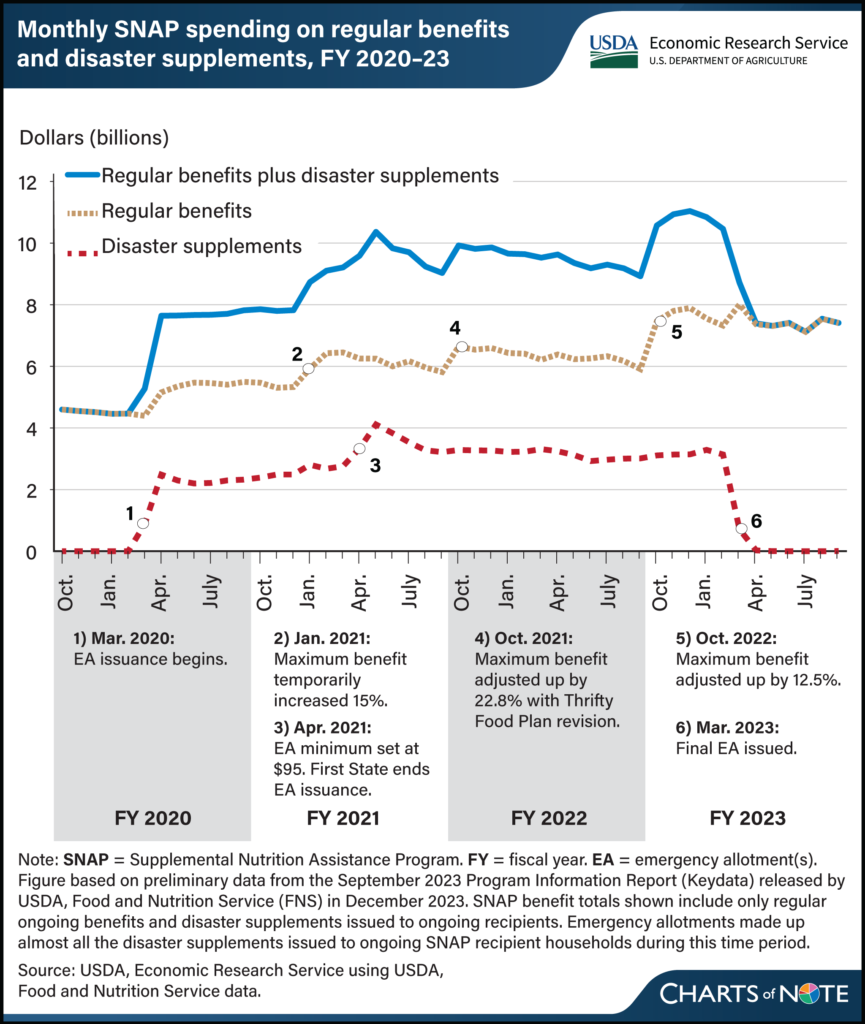
4. Benefit Adjustments for Cost-of-Living Increases
One positive change under the new rules is the adjustment of SNAP benefit levels to account for the rising cost of food and living expenses. This means that monthly SNAP benefits will be adjusted to reflect inflation and the increased cost of groceries. As prices at the supermarket continue to rise, these adjustments will help ensure that benefits keep pace with the real cost of food.
For example, a family of four might see an increase in their monthly SNAP benefit, helping them better manage their grocery expenses. These changes are particularly important for low-income families, who often feel the impact of rising food prices the most.
The increase in benefit levels is intended to make sure that recipients can purchase enough food to meet their needs. However, benefit amounts will still vary depending on household size, income, and location. It’s important to check your eligibility each year to understand how the new benefit amount applies to you.
5. Administrative Changes: Impact on Access to Benefits
The administrative structure of SNAP will also change starting in 2026. Federal policy changes will shift more administrative costs to states, meaning that states will have more flexibility in how they administer the program. While this might offer some benefits, it could also lead to variations in service and delays in processing applications.
The shift in administration means that each state will have its own specific process for applying, recertifying, and receiving benefits. Some states may implement more efficient procedures, while others might face delays as they adjust to these changes.
It is essential to stay informed by contacting your local SNAP office to understand the specific procedures in your state. Being aware of how these changes might affect you can help you avoid delays in receiving your benefits.
6. Additional Resources and How to Stay Informed
In addition to SNAP, there are other resources that can assist you with food insecurity:
- WIC (Women, Infants, and Children): Provides nutrition assistance to low-income pregnant women, infants, and children under the age of five.
- Local food banks: Many communities have food banks that provide free or low-cost food to individuals and families in need.
- Meals on Wheels: For elderly or homebound individuals, Meals on Wheels offers food delivery services.
You can also check with your local community centers, religious organizations, and government services for additional resources. These organizations can provide short-term help and support until you are able to meet the SNAP eligibility requirements.
$2000 Stimulus Check in January 2026: Check Eligibility, and Payment Status
$2,000 Direct Deposits Are Official — IRS Sets Start Date for Massive Payouts
Federal $2000 Deposits Coming in January 2026: Guide for Eligible Beneficiaries