![Pilot Spotlight How [Pilot Name] Protects Their Home Waters](https://seaplanesandais.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Pilot-Spotlight-How-Pilot-Name-Protects-Their-Home-Waters-1024x576.jpg)
How [Pilot Name] Protects Their Home Waters: Navigating the waters of the United States takes real skill—especially when those waters are your home turf. Maritime pilots like [Pilot Name] do more than just steer big ships through tricky routes. They protect the environment, keep local waters safe from accidents, and make sure the marine ecosystem stays healthy for future generations. Whether they’re guiding massive oil tankers or cruise liners, pilots hold a critical responsibility to protect their home waters with expertise, care, and a sense of duty.
Pilots serve as local legends of the sea, combining years of experience with deep knowledge of coastal waters to prevent accidents, spills, and pollution. This article breaks down how these maritime pros safeguard waterways, why their role matters for environmental sustainability, and practical steps they take every day to keep our waters safe.
Table of Contents
How [Pilot Name] Protects Their Home Waters
Maritime pilots like [Pilot Name] are unsung heroes who protect the security and health of America’s home waters every single day. Their deep local expertise, skillful navigation, and commitment to environmental stewardship keep our ports running safely while defending the delicate ecosystems we rely on. Protecting home waters is not just a job—it’s a legacy. By understanding and supporting their vital work, we help ensure clean, safe seas for generations to come.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Role of Maritime Pilot | Navigates large vessels safely through local waters |
| Environmental Protection | Prevents marine pollution, oil spills, invasive species |
| Economic Impact | Reduces fuel waste and operational costs for shipping |
| Safety Statistics (U.S. Waters) | Pilots reduce maritime incidents significantly |
| Training & Licensing | Pilots undergo rigorous testing and certification |
| EPA Water Quality Data | 35% of US river miles rated good, 29% poor condition |
What is a Maritime Pilot?
At the heart of the waterways, a maritime pilot is an experienced mariner responsible for navigating ships through hazardous, congested, or environmentally sensitive parts of U.S. waters. Unlike the ship’s captain who commands the vessel, the pilot temporarily comes aboard to steer the ship safely through these tricky passages. This in-the-know pro knows every twist and turn like the back of their hand.
In the U.S., pilots work in ports, coastal regions, and large freshwater bodies like the Great Lakes, playing a huge part in protecting American waters from accidents and pollution. They’re not just pilots—they’re environmental guardians, ensuring that every move they make helps safeguard marine life and habitats.
The Importance of Protecting Home Waters
Our watery borders are more than just traffic lanes—they’re ecosystems teeming with life. The health of these ecosystems impacts fish stocks, water quality, and the well-being of coastal communities. Pilots protect these waters by minimizing navigation errors that might cause oil spills, collisions, or illegal discharge of waste.
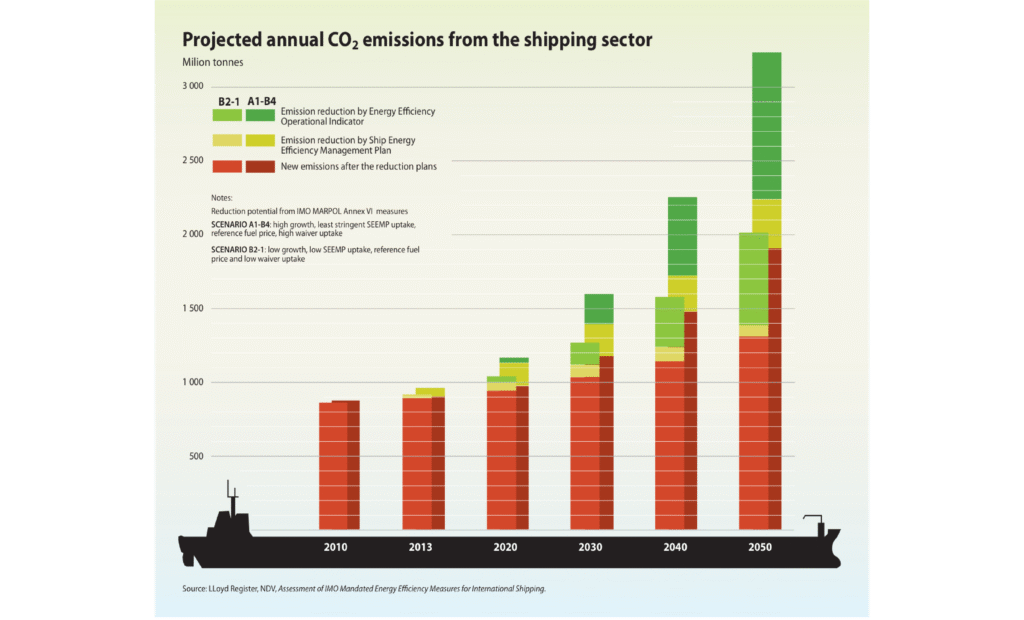
Consider that maritime shipping accounts for approximately 3% of global greenhouse emissions. Effective pilotage can help reduce fuel consumption by optimizing ship movements, directly impacting emissions in the U.S. coastal zones. This green approach isn’t just good for the environment—it saves money and improves port efficiency. Pilots often coordinate with tugboats and port officials to ensure operations are smooth, reducing risks of accidents and pollution release.
How Do Pilots Protect the Home Waters?
Expert Navigation to Avoid Spills and Accidents
By guiding massive vessels through narrow channels and busy harbors, pilots use their training to avoid groundings and collisions that can cause catastrophic oil or hazardous chemical spills. In many cases, they board vessels moving at sea via rope ladder—a risky, skilled operation itself—demonstrating sheer mastery and dedication.
Monitoring and Reporting Pollution
Pilots keep an eagle eye on any signs of illegal pollution, such as unauthorized discharges or fuel leaks. They are legally obligated to report violations to authorities, reinforcing marine environmental laws and stewardship. This also includes monitoring ballast water discharge to prevent invasive species from disrupting local ecosystems.
Coordination and Communication
Using advanced communication tools and cooperating closely with tugs, harbor masters, and port authorities ensures vessels maneuver with precision, reducing unnecessary fuel burn and the footprint left behind. New technologies like shore power (cold ironing) help vessels cut down engine use when docked, and pilots advocate and implement these greener practices.
Advanced Technologies in Pilotage
Technology has revolutionized how pilots protect home waters. Modern navigation systems integrate GPS, radar, and Electronic Chart Display Information Systems (ECDIS), allowing pilots to plan the safest and most efficient paths through narrow waterways. Pilot boats are equipped with state-of-the-art communication gear to maintain constant contact with ports and ships.
Environmental sensors on pilot boats monitor water quality in real time, detecting pollution or harmful conditions early. Some pilots use drones to survey vulnerable coastal ecosystems and check for illegal dumping, enhancing their vigilance beyond traditional methods.
Training and Licensing: Not Your Average Job
Becoming a licensed maritime pilot requires years of time on the water, specialized training, and passing rigorous exams. For example, the Washington State Board of Pilotage Commissioners oversees standards to ensure pilots have deep local knowledge and can protect lives and property while minimizing environmental harm.
Pilots train constantly to stay updated on marine traffic laws, environmental regulations, and emerging technologies. Their expertise spans ship handling, weather analysis, emergency readiness, and pollution control—a commitment to excellence that benefits every stakeholder.
Environmental Impact and Statistics
- According to the Marine-Pilots.com research, skilled pilotage contributes to reducing emissions by optimizing ship trajectories and speeds, which can lower fuel consumption and harmful greenhouse gases.
- The EPA’s National Rivers and Streams Assessment reveals that roughly 35% of river and stream miles in the U.S. are rated good for fish communities, highlighting areas where pilots’ protective actions contribute to water quality.
- Conversely, about 29% of river miles are in poor condition, emphasizing the continual need for vigilance in protecting home waters from pollution and human impact.
Community Involvement and Advocacy
Many pilots engage directly with coastal communities and environmental groups, educating the public on marine safety and conservation. Pilots like [Pilot Name] often participate in local beaches and harbor clean-up projects, ensuring the areas they know best remain pristine. They advocate for policies that promote sustainable shipping practices and stricter pollution controls.
This community engagement amplifies their impact beyond the bridge of a ship, fostering a culture of respect for maritime environments among all stakeholders.
Practical Advice from the Pilot’s Playbook
If you’re a coastal professional, environmental steward, or just curious, here’s how pilots and those involved with marine navigation protect waters:
- Invest in Training: Follow pilot programs or certifications that emphasize safety and environmental awareness.
- Use Technology: Employ real-time navigation systems and emission reduction tools.
- Report Violations: If you witness pollution or unsafe shipping behavior, notify authorities.
- Promote Green Practices: Encourage ports to adopt clean energy and low-emission vessel policies.
- Stay Educated: Understand local marine ecosystems to appreciate the impact decisions at sea can have.
State-by-State AIS Regulations: A Seaplane Pilot’s Compliance Guide
A Pilot’s 10-Point Inspection Checklist for Aquatic Invasive Species (AIS)




![Case Study How [Lake Association] Partners with Pilots to Stop AIS](https://seaplanesandais.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Case-Study-How-Lake-Association-Partners-with-Pilots-to-Stop-AIS-300x169.jpg)











